Troubleshooting areas v7
The following topics provide information on specific problem areas you may encounter.
Removing Java can remove Replication Server
When Replication Server is installed on a machine where Java is not present, the JDK is installed as part of the installation process. In this situation the JDK is installed as a dependency of the Replication Server. If you subsequently remove the JDK, Replication Server is also removed.
If Java 1.8 or greater existed before Replication Server was installed, removing the JDK does not remove the Replication Server.
Java runtime errors
If errors are encountered regarding the Java Runtime Environment such as the Java program cannot be found or Java heap space errors, check the parameters set in the Replication Server configuration file xdbReplicationServer-xx.config. See Replication Server configuration file for information on this file.
The following is an example of the content of the Replication Server Configuration file:
#!/bin/sh JAVA_EXECUTABLE_PATH="/usr/bin/java" JAVA_MINIMUM_VERSION=1.8 JAVA_BITNESS_REQUIRED=64 JAVA_HEAP_SIZE="-Xms2048m -Xmx4096m" PUBPORT=9051 SUBPORT=9052
After you make any changes to the parameters in the Replication Server configuration file, be sure to restart the publication server and subscription server.
Starting the publication server or subscription server
Note
The subscription server applies only to single-master replication systems.
If you can't start the publication server or the subscription server:
Check the
pubserver.logandsubserver.logfiles for errors.Check the log file of the database server running the controller database for errors.
Verify that the user name and password in the Replication Server configuration file on the hosts running the publication server and subscription server match a database user name and password in the database server running the controller database that the publication server and subscription server are attempting to access.
If the controller database is a Postgres database, verify that the
pg_hba.conffile of its Postgres database server has entries that allow access to the controller database from the IP addresses of the hosts running the publication server and subscription server by the user name in the Replication Server configuration file.
Deleting the control schema and control schema objects
The control schema completely describes the replication system. The control schema and its control schema objects must be complete and correct for replication to occur properly. In addition, the configuration and maintenance operations performed through the Replication Server console or the Replication Server CLI can't be accomplished properly unless the control schema is complete and correct.
There might be occasions in which the control schema becomes corrupted. Either one or more control schema tables containing metadata are inadvertently deleted, or the data in the control schema tables becomes corrupted. Typically, corruption occurs in the form of the first case: one or more control schema tables were deleted, or the entire control schema and its contents were deleted manually using an SQL utility rather than through the operation of the Replication Server console or Replication Server CLI.
In these situations, there might be no other choice but to remove all of the remaining control schema objects using the database management system’s deletion functions, which effectively deletes all replication systems managed by the control schema.
The same control schema deletion procedure must be performed in all publication databases that share the same control schema information as the current controller database given in the Replication Server configuration file.
From the viewpoint of the Replication Server console replication tree, a publication server that connects to the controller database has subordinate to it the publication databases sharing the same control schema information.
In the following example, the SMR publication database edb as well as the three MMR primary node databases mdnnode, MMRnode_a, and MMRnode_b are all managed by the same publication server, which connects to the controller database designated in the Replication Server configuration file. Thus, all publication databases edb, mdnnode, MMRnode_a, and MMRnode_b contain what should be the same control schema information.
The control schema must be removed from all four publication databases if it is determined that the control schema is corrupted in any of the four publication databases.
Finally, the subscription databases of SMR systems contain a control schema object, which must be deleted as well.
In the preceding example, subscription database subdb contains a control schema object that might have to be deleted if control schema deletion is performed on the publication database.
These instructions describe how to completely remove all control schema objects created by the Replication Server product, leaving just your original publication tables and any replicated subscription tables or publication tables of multi-master system nodes. Hence, the definition and framework for all existing single-master and multi-master replication systems are deleted. In effect, this simulates the situation when you install the Replication Server product for the first time.
After you perform this deletion process, you must recreate single-master replication systems following the directions in Creating a publication onward. You must recreate a multi-master replication system following the directions in Creating a publication onward.
Don't attempt this if any replication systems are running in production. All replication systems will become inoperable. This section describes what to look for to tell if the control schema isn't complete, and, if so, what to delete to completely remove the replication system. This section doesn't discuss the internal contents of the control schema objects. If all of the control schema objects are present, then review the checklist in Common problems checklist before proceeding with deleting the control schema, as it is fairly unlikely that the content of a control schema table becomes corrupted.
If you decide that you must delete all of the control schema objects:
Stop the publication server.
Stop the subscription server.
Look for the control schema objects contained in a publication database. In the example used in this section, pubuser is the publication database user name. The publication consists of two tables: dept and emp.
For Oracle only: See Oracle control schema objects for a list of Oracle control schema objects.
For SQL Server only: See SQL control schema objects for a list of SQL Server control schema objects.
For Postgres only: See PostgreSQL control schema objects for a list of Postgres control schema objects.
If the schema that is supposed to contain the control schema objects (the publication database user name for Oracle or the control schema you created or selected when configuring a SQL Server publication database along with
_edb_replicator_pub,_edb_replicator_sub, and_edb_scheduler, or_edb_replicator_pub, _edb_replicator_sub, and_edb_schedulerfor Postgres) is missing, or there are missing database objects under the control schema, then you might need to complete the process of removing all remaining control schema objects.If you decide to undergo this procedure, you must remove the control schema objects from all publication databases. You must also remove all subscription metadata objects from the subscription databases. Proceed with Step 7 and repeat Step 7 for all publication databases. Then proceed with Step 8 and repeat Step 8 for all subscription databases.
If the control schema objects look intact, repeat Step 3 for all other publication databases. If the control schema objects of all publication databases appear intact, then proceed with Step 5.
For single-master replication systems, the subscription database contains a single control schema object in the form of a table named
rrep_txset_health. See Subscription metadata object for a listing of this control schema object for each type of subscription database.For each subscription database, verify the presence of this subscription metadata object.
If, at this point, all control schemas and control schema objects appear intact in all publication databases and all subscription databases, then chances are that the problem lies elsewhere. Don't proceed with any further steps in this section. Instead, recheck the checklist in Common problems checklist.
If it was determined that incomplete control schema objects exist, and you decide to go ahead with the deletion process, proceed with Step 7.
Repeat this step for every publication database to delete its control schema and control schema objects.
For Oracle only: If the publication user name still exists, then log onto SQL*Plus or any other Oracle database administration utility and drop all control schema objects owned by the publication user. Alternatively, you can drop the publication database user along with its database objects using the cascade option, but the publication database user must be recreated and privileges reassigned if you intend to rebuild your replication systems. See Preparing the publication database for directions on creating the publication database user. The following example illustrates use of the cascade option:
SQL> CONNECT system/password Connected. SQL> DROP USER pubuser CASCADE; User dropped.
For SQL Server only: If any of the control schema objects listed in Step 3 still exist, then log onto the SQL Server command line program, sqlcmd, or SQL Server Management Studio and drop these objects. The following example assumes some of the control schema objects were created under schema
pubuser. The other control schema objects are created under_edb_replicator_pub, _edb_replicator_sub,and_edb_scheduler. The publication tables aredeptandemplocated in schemaedb.The following example shows how to delete the jobs in the
msdbdatabase:1> USE msdb; 2> GO Changed database context to 'msdb'. 1> EXEC sp_delete_job @job_name = 'rrep_cleanup_job_edb'; 2> GO 1> EXEC sp_delete_job @job_name = 'rrep_txset_job_edb'; 2> GO The next example shows the deletion of the triggers on the non-snapshot only publication tables: 1> USE edb; 2> GO Changed database context to 'edb'. 1> DROP TRIGGER edb.rrpd_edb_dept; 2> DROP TRIGGER edb.rrpi_edb_dept; 3> DROP TRIGGER edb.rrpu_edb_dept; 4> DROP TRIGGER edb.rrpd_edb_emp; 5> DROP TRIGGER edb.rrpi_edb_emp; 6> DROP TRIGGER edb.rrpu_edb_emp; 7> GO
The control schema objects under the
_edb_replicator_pubschema are dropped as shown by the following:1> USE edb; 2> GO Changed database context to 'edb'. 1> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_lock; 2> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_MMR_pub_group; 3> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_MMR_txset; 4> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_properties; 5> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_publication_subscriptions; 6> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_publication_tables; 7> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_tables; 8> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_tx_monitor; 9> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_txset; 10> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_txset_health; 11> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_txset_log; 12> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_cleanup_conf; 13> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_conflicts; 14> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_conflicts_options; 15> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_events; 16> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_events_status; 17> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_MMR_pub_group; 18> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_pub_database; 19> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_pub_table_replog; 20> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_pub_replog; 21> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_publication_filter; 22> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_publication_filter_rule; 23> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_publication_subscriptions; 24> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_publications; 25> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_pubtables_ignoredcols; 26> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_pub.xdb_sub_servers; 27> GO
For SQL Server 2014 only: Drop the following control schema objects when the publication database is SQL Server 2014:
1> USE edb; 2> GO Changed database context to 'edb'. 1> DROP SEQUENCE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_tx_seq; 2> DROP SEQUENCE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_txset_seq; 3> DROP SEQUENCE _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_common_seq; 4> GO
Drop the
_edb_replicator_pubcontrol schema:1> USE edb; 2> GO
Changed database context to
edb.1> DROP SCHEMA _edb_replicator_pub; 2> GO
The control schema objects under the
_edb_replicator_subschema as well as the schema itself are dropped as shown by the following.Note
(For SQL Server 2014): When the publication database is SQL Server 2014, the first table in the following list,
rrep_common_seq, does not exist. Therefore don't issue the firstDROP TABLE_edb_replicator_sub.rrep_common_seqcommand.1> USE edb; 2> GO Changed database context to 'edb'. 1> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_sub.rrep_common_seq; 2> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_sub.xdb_sub_database; 3> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_sub.xdb_subscription_tables; 4> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_sub.xdb_subscriptions; 5> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_sub.xdb_tables; 6> DROP SCHEMA _edb_replicator_sub; 7> GO
The control schema objects under the
_edb_schedulerschema as well as the schema itself are dropped as shown by the following:1> USE edb; 2> GO Changed database context to 'edb'. 1> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_BLOB_TRIGGERS; 2> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_CALENDARS; 3> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_CRON_TRIGGERS; 4> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_SIMPLE_TRIGGERS; 5> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_TRIGGER_LISTENERS; 6> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_FIRED_TRIGGERS; 7> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_TRIGGERS; 8> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_JOB_LISTENERS; 9> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_JOB_DETAILS; 10> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_LOCKS; 11> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_PAUSED_TRIGGER_GRPS; 12> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_SCHEDULER_STATE; 13> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_sub_BLOB_TRIGGERS; 14> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_sub_CALENDARS; 15> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_sub_CRON_TRIGGERS; 16> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_sub_SIMPLE_TRIGGERS; 17> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_sub_TRIGGER_LISTENERS; 18> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_sub_FIRED_TRIGGERS; 19> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_sub_TRIGGERS; 20> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_sub_JOB_LISTENERS; 21> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_sub_JOB_DETAILS; 22> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_sub_LOCKS; 23> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_sub_PAUSED_TRIGGER_GRPS; 24> DROP TABLE _edb_scheduler.sch_sub_SCHEDULER_STATE; 25> DROP SCHEMA _edb_scheduler; 26> GO
The control schema objects under the
pubuserschema are dropped as shown by the following:1> USE edb; 2> GO Changed database context to 'edb'. 1> DROP FUNCTION pubuser.getPackageVersionNumber; 2> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.CleanupShadowTables; 3> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.ConfigureCleanUpJob; 4> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.ConfigureCreateTxSetJob; 5> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.CreateMultiTxSet; 6> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.CreateTableLogTrigger; 7> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.CreateTxSet; 8> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.CreateTxSet_old; 9> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.CreateUniTxSet; 10> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.GetNewTxsCount; 11> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.JobCleanup; 12> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.JobCreateTxSet; 13> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.LoadPubTableList; 14> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.RemoveCleanupJob; 15> DROP PROCEDURE pubuser.RemoveCreateTxSetJob; 16> DROP TABLE pubuser.rrst_edb_dept; 17> DROP TABLE pubuser.rrst_edb_emp; 18> GO
For Postgres only: If any of the schemas
_edb_replicator_pub,_edb_replicator_sub, or_edb_schedulerstill exist in the publication database, drop the schema and all of its database objects. The following example shows a connection established in psql to the publication database edb. TheDROP SCHEMA CASCADEstatement is then used to drop the schemas.edb=# \c edb enterprisedb You are now connected to database "edb" as user "enterprisedb". edb=# DROP SCHEMA _edb_replicator_pub CASCADE; NOTICE: drop cascades to 51 other objects DETAIL: drop cascades to sequence _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_common_seq drop cascades to sequence _edb_replicator_pub.rrep_tx_seq . . . DROP SCHEMA edb=# DROP SCHEMA _edb_replicator_sub CASCADE; NOTICE: drop cascades to 9 other objects DETAIL: drop cascades to sequence _edb_replicator_sub.rrep_common_seq drop cascades to table _edb_replicator_sub.xdb_sub_database . . . DROP SCHEMA edb=# DROP SCHEMA _edb_scheduler CASCADE; NOTICE: drop cascades to 40 other objects DETAIL: drop cascades to table _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_job_details drop cascades to table _edb_scheduler.sch_pub_job_listeners . . . DROP SCHEMA
For synchronization replication with the trigger-based method, in the schema containing the publication tables, drop the triggers and trigger functions associated with the publication tables:
edb=# SET search_path TO edb; SET edb=# DROP FUNCTION rrpd_edb_dept_tgfunc() CASCADE; NOTICE: drop cascades to trigger rrpd_edb_dept on table dept DROP FUNCTION edb=# DROP FUNCTION rrpi_edb_dept_tgfunc() CASCADE; NOTICE: drop cascades to trigger rrpi_edb_dept on table dept DROP FUNCTION edb=# DROP FUNCTION rrpu_edb_dept_tgfunc() CASCADE; NOTICE: drop cascades to trigger rrpu_edb_dept on table dept DROP FUNCTION edb=# DROP FUNCTION rrpd_edb_emp_tgfunc() CASCADE; NOTICE: drop cascades to trigger rrpd_edb_emp on table emp DROP FUNCTION edb=# DROP FUNCTION rrpi_edb_emp_tgfunc() CASCADE; NOTICE: drop cascades to trigger rrpi_edb_emp on table emp DROP FUNCTION edb=# DROP FUNCTION rrpu_edb_emp_tgfunc() CASCADE; NOTICE: drop cascades to trigger rrpu_edb_emp on table emp DROP FUNCTION
Repeat this step for every subscription database to delete its control schema and control schema object.
For single-master replication systems, the subscription database contains a single control schema object in the form of a table named
rrep_txset_health. Delete this table in all subscription databases. For SQL Server and Postgres subscription databases, delete the parent schema _edb_replicator_sub as well.For Oracle subscription databases, the parent schema isn't generated by Replication Server, so it's your decision as to whether to keep or delete the parent schema.
For Oracle only: The
RREP_TXSET_HEALTHtable is created in the subscription database user’s schema. Drop this table.SQL> CONNECT subuser/password Connected. SQL> DROP TABLE rrep_txset_health; Table dropped.
For SQL Server only: The
rrep_txset_healthtable is created in the schema named _edb_replicator_sub. Drop this table and schema.1> USE subdb; 2> GO Changed database context to 'subdb'. 1> DROP TABLE _edb_replicator_sub.rrep_txset_health; 2> GO 1> DROP SCHEMA _edb_replicator_sub; 2> GO
For Postgres only: The
rrep_txset_healthtable is created in the schema named_edb_replicator_sub. Drop this table and schema.edb=# \c subdb enterprisedb You are now connected to database "subdb" as user "enterprisedb". subdb=# DROP SCHEMA _edb_replicator_sub CASCADE; NOTICE: drop cascades to table _edb_replicator_sub.rrep_txset_health DROP SCHEMA
In the Replication Server configuration file, delete the lines containing the following parameters:
user,password,host,port,database, andtype.Keep the lines with the following parameters:
admin_user,admin_password, andlicense_key(if it exists).See Replication Server configuration file for information on the Replication Server configuration file. See Installation details for the file system location of the Replication Server configuration file.
The absence of these parameters prevents the publication server and subscription server from attempting to connect to this database upon publication and subscription server startup.
The Replication Server configuration file appears as follows without the controller database connection and authentication information:
#xDB Replication Server Configuration Properties #Fri Jan 30 17:34:06 GMT-05:00 2015 admin_password=ygJ9AxoJEX854elcVIJPTw\=\= admin_user=enterprisedb
Start the publication server.
Start the subscription server.
The replication tree appears as follows:
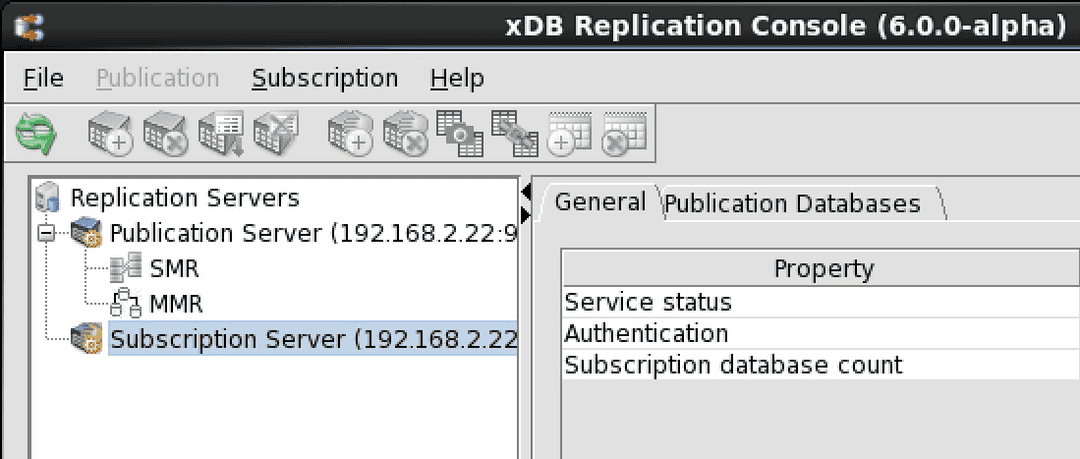
All the nodes under the SMR and MMR type nodes beneath the Publication Server node and under the Subscription Server node no longer appear.
Recreate the replication system as described in Creating a publication onward for a single-master replication system. See Creating a publication for a multi-master replication system.
Dropping replication slots for log-based synchronization replication
As described in Logical replication slots logical replication slots are used for the log-based method of synchronization replication. While a log-based replication system is in use, these replication slots remain connected to the Postgres databases. When the replication system is removed, these replication slots are also deleted.
There are circumstances when you want to drop a Postgres database used in a replication system but the replication system can't be removed according to the normal procedure of using the Replication Server console or the Replication Server CLI. In such cases, it is assumed that the replication system has somehow become corrupted, and you want to delete the replication system components, including some of the databases used in the replication system.
When the log-based method is used, certain additional procedures might be required to remove the replication slots before dropping the databases. Postgres doesn't permit a database to be dropped if a replication slot is connected to it. The following describes how you cam remove the replication slots to drop a database.
Warning
Don't attempt this if any replication systems are running in production. All replication systems will become inoperable.
Replication slots can be displayed by the following query on the database server containing the databases to be dropped:
edb=# SELECT slot_name, slot_type, database, active, active_pid FROM pg_replication_slots;
slot_name | slot_type | database | active | active_pid -------------+-----------+----------+--------+------------ xdb_14793_5 | logical | edb | t | 5288 xdb_79910_5 | logical | MMRnode | t | 5327 (2 rows)
The active column indicates whether the replication slot is active. To deactivate an active replication slot, first stop the publication server. If the active column of the replication slot now displays f for false then you can remove the replication slot.
If the replication slot is still active, then you can deactivate it by terminating the process shown in the active_pid column with the following command:
edb=# SELECT pg_terminate_backend(5327);
pg_terminate_backend ---------------------- t (1 row)
The following now shows that replication slot xdb_79910_5 for database MMRnode was deactivated:
edb=# SELECT slot_name, slot_type, database, active, active_pid FROM pg_replication_slots;
slot_name | slot_type | database | active | active_pid -------------+-----------+----------+--------+------------ xdb_14793_5 | logical | edb | t | 5288 xdb_79910_5 | logical | MMRnode | f | (2 rows)
Drop the replication slot with the following command by specifying the slot name:
edb=# SELECT pg_drop_replication_slot('xdb_79910_5');
pg_drop_replication_slot -------------------------- (1 row)
Now, the dropped replication slot doesn't appear when the pg_replication_slots directory is queried:
edb=# SELECT slot_name, slot_type, database, active, active_pid FROM pg_replication_slots;
slot_name | slot_type | database | active | active_pid -------------+-----------+----------+--------+------------ xdb_14793_5 | logical | edb | t | 5288 (1 row)
The database can now be successfully dropped:
edb=# DROP DATABASE MMRnode;
DROP DATABASE
In addition, you can display replication origins with the following command:
edb=# SELECT * FROM pg_replication_origin;
roident | roname
---------+-----------------------
1 | xdb_MMRnode_emp_pub_1
2 | xdb_edb_emp_pub_6
(2 rows)You can use the following command to remove a replication origin:
edb=# SELECT pg_replication_origin_drop('xdb_MMRnode_emp_pub_1');
pg_replication_origin_drop ---------------------------- (1 row)
The following shows this replication origin was removed:
edb=# SELECT * FROM pg_replication_origin;
roident | roname
---------+-----------------------
2 | xdb_edb_emp_pub_6
(1 row)For more information on logical decoding functions see 9.26.6 Replication Functions under Section 9.26 System Administration Functions in the PostgreSQL core documentation.
After performing this process, it is unlikely that you can remove the entire replication system with the Replication Server console or Replication Server CLI. You must remove the remaining replication system components manually. Part of this process is removing the control schema and control schema objects from the publication databases. See Dropping replication slots for log-based synchronization replication for information on this procedure.